Latency is the expression of the time it takes for a packet of data to travel from a source to a specific destination and back to the source. Latency is expressed in a millisecond. The higher the Ping is, the higher the delay on the network. Therefore, low latency implies low to zero delays, thus giving a positive user experience (UX).
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is responsible for application programs and computing device exchange of data and messages over a network. The speed of sending packets across the internet and the success of data and message delivery rely on the rate of latency. Generally, an acceptable latency is about 20 to 100 milliseconds. If TCP has high latency, it is more likely to have a lag from the users’ end.
Table of Contents
What causes TCP latency?
Higher latency means poor user experience. It is very frustrating to have lags while in the middle of a game, an important meeting, call, etc. Therefore, it is important to understand the cause of the delay to fix the source of high latency. Here are the top reasons for high latency:
Non-network related causes of high TCP latency
- Misconfigured or faulty DNS server
- Poorly optimized or over-utilized backend database
- Low memory or CPU cycles of the end-user device
- Geographical location
- Configuration of firewalls
Network related causes of high TCP latency
- The number of hops or distance between source and destination
- Network bottlenecks
- QoS that’s non-existent or ineffective
- Network device CPU/Memory spikes
- Suboptimal routing
- Internet service provider (ISP) quality (Wired vs. Wi-Fi)
- Faulty in-line devices
How do I fix high TCP latency?
Step 1: Have a fixed line
As latency rate influences the TCP, it is paramount to reduce network latency as much as possible. A wired connection is more stable than a WiFi connection. Also, consider the connection type between copper and fiber optics.
Step 2: Check the bandwidth
Run a test to see if you are getting enough bandwidth. If not, contact your ISP to optimize the speeds. Also, check users within your network who are using up all the bandwidth or have heavy downloads or streaming, causing an increase in latency.
Step 3: Reboot the router
A router can become strained as well for continued use. Thus, restarting your router will refresh your internet connection and latency rate.
Step 4: Firewall configuration
A firewall that directly monitors web traffic will increase the latency if not properly configured. Add an exception within the firewall settings for a specific service you want to use in open traffic.
Step 5: Choose a server that is geographically closer to you
Low latency or high latency depends on your distance to the server. Thus, choosing a server that is geographically closer to you would help in improving latency.
Step 6: Use a WAN optimizer
WAN optimizers tunes and optimizes an Internet connection
How does latency affect TCP?
Latency is a major factor in TCP performance
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is responsible for application programs and computing device exchange of data and messages over a network. The higher the latency is, the slower the data transfer. Therefore, high latency implies an infuriating user experience. High manifest in lag, which delays the performance of a system.
Generally, the acceptable latency is between 20 ms to 100 ms. The lower the latency is, the faster the data transfer. There are tons of ways to improve TCP latency. Determine whether high TCP latency is caused by a network or non-network issue, then you can start finding the best fix for you.
How can you improve the performance of TCP in WIFI?
A WiFi connection has more interference than a wired connection affecting the latency of your TCP. Here are some considerations to improve TCP latency for WiFi connection:
- Find the best WiFi frequency band for your router
- Hardwire with an ethernet connection
- Update/upgrade network hardware
- Restart the router to refresh the connection and latency
- Move closer to the modem
How do you optimize TCP?
Optimizing TCP prevents overloading the network or receivers, thus improving the performance of the delivery of packets. Here are a few steps on how to optimize TCP
Windows 10 TCP optimization
Step 1: Download TCP Optimizer
Step 2: Insert your internet speed into the TCP Optimizer. Set the speed to the maximum speed that your ISP offers.
Step 3: From the Choose settings section, choose Optimal, then apply changes.
Step 4: A pop-up window will appear. Check the Backup and Create Log boxes and hit okay.
Step 5: Reboot to apply changes
Mac TCP optimization
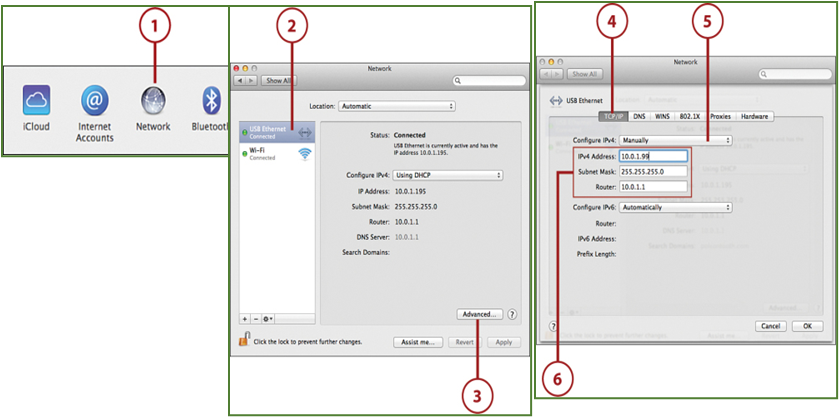
Step 1: Choose the Apple menu
Step 2: Select System Preferences
Step 3: Click Network, select a network service in the list on the left
Step 4: Click Advanced, then click TCP/IP.
Step 5: Use the Configure IPv4 drop-down menu to change your settings to configure manually.
Step 6: Enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Router.